
| Farragut class | DESTROYERS | |
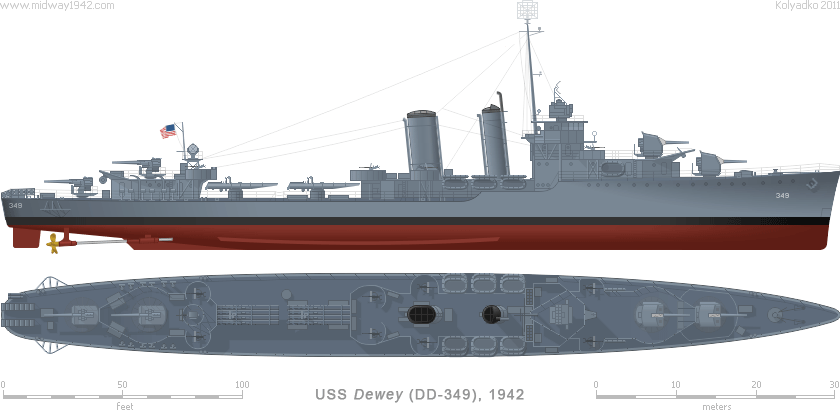
| Displacement: | 2,307 t (1,358 t Std) | Machinery: | 4 boilers, 2 shafts | DP Guns: | 4×1×5 in (127 mm)/38 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Length: | 341 ft 3 in | 104 m | Max Power: | 42,800 hp | 31 916 kW | AA Guns: | 8×1×.79 in (20 mm) | |||||
| Beam: | 34 ft 3 in | 10.4 m | Max Speed: | 37 kts | 68.5 km/h | Torpedo Battery: | 2×4×21 in (533 mm) | |||||
| Draght: | 16 ft 6 in | 4.7 m | Range: | 6,500 nm | 12 000 km | Depth Charges: | 2 roller racks, 12 throwers | |||||
| Complement: | 251 officers & enlisted | Bunkerage: | 600 t fuel oil | Sensors: | Surface and air radars, sonar | |||||||
* Armament as during the Battle of Midway (June 1942).
After building a great number (273 ships) of Caldwell, Clemson and Wickes classes destroyers between 1917 and 1922 the line of destroyers development in the U.S. Navy has interrupted for more than ten years, thereby to the beginning of 1930s the “flushdeckers”, making a basis of light naval forces, have become outdated. Designed in 1931 Farragut class destroyers were the first class of the new generation of U.S. destroyers, significantly surpassed their predecessors in speed, maneuverability, seaworthiness, range, armament, and habitability.
The Farragut class destroyers were initially armed with eight 21 in (533 mm) torpedo tubes in two quadruple centerline mounts, five 5 in (127 mm) dual-purpose guns (the forward two shielded against the weather, the others open), and four .50 in (12.7 mm) AA machine guns. By the middle of 1935, all eight ships had been refitted with two depth charge roller racks and storage, indicating the necessity of providing the fleet with anti-submarine warfare methods. As wartime necessity indicated that more, and heavier AA was not only desirable but a matter of life-and-death, the no. 3 gun was removed, making available weight and space for the installation of radar systems, two 1.57 in (40 mm) Bofors twin mounts and six .79 in (20 mm) Oerlikon autocannons instead of four .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns, but for lack of Boforses they were replaced by two more Oerlikons. Anti-submarine armament was also reinforced with K-type depth charge throwers.
Four Farragut class destroyers (DD-349 Dewey, DD-352 Worden, DD-354 Monaghan, DD-355 Aylwin) took part in the Battle of Midway as a Fueling group escort and a part of Task Force 16 Destroyer Screen (Task Group 16.4).
| Ship | Builder | Laid Down | Launched | Commisioned | Fate | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD-348 | Farragut | Bethlehem Steel Corp. Quincy, MA | 20 | Sep | 1932 | 15 | Mar | 1934 | 18 | Jun | 1934 | Sold for scrap | 14 | Aug | 1947 | |||
| DD-349 | Dewey | Bath Iron Works. Bath, ME | 16 | Dec | 1932 | 28 | Jul | 1934 | 4 | Oct | 1934 | Sold for scrap | 20 | Dec | 1946 | |||
| DD-350 | Hull | U. S. Navy Yard. New York, NY | 7 | Mar | 1933 | 31 | Jan | 1934 | 11 | Jan | 1935 | Sunk in storm | 18 | Dec | 1944 | |||
| DD-351 | Macdonough | U. S. Navy Yard. Boston, MA | 15 | May | 1933 | 22 | Aug | 1934 | 15 | Mar | 1935 | Sold for scrap | 20 | Dec | 1946 | |||
| DD-352 | Worden | U. S. Navy Yard. Puget Sound, WA | 29 | Dec | 1932 | 27 | Oct | 1934 | 15 | Jan | 1935 | Grounded | 12 | Dec | 1943 | |||
| DD-353 | Dale | U. S. Navy Yard. New York, NY | 10 | Feb | 1934 | 23 | Jan | 1935 | 17 | Jun | 1935 | Sold for scrap | 20 | Dec | 1946 | |||
| DD-354 | Monaghan | U. S. Navy Yard. Boston, MA | 21 | Nov | 1933 | 9 | Jan | 1935 | 19 | Apr | 1935 | Sunk in storm | 18 | Dec | 1944 | |||
| DD-355 | Aylwn | U. S. Navy Yard. Philadelphia, PA | 23 | Sep | 1933 | 10 | Jul | 1934 | 1 | Mar | 1935 | Sold for scrap | 20 | Dec | 1946 | |||